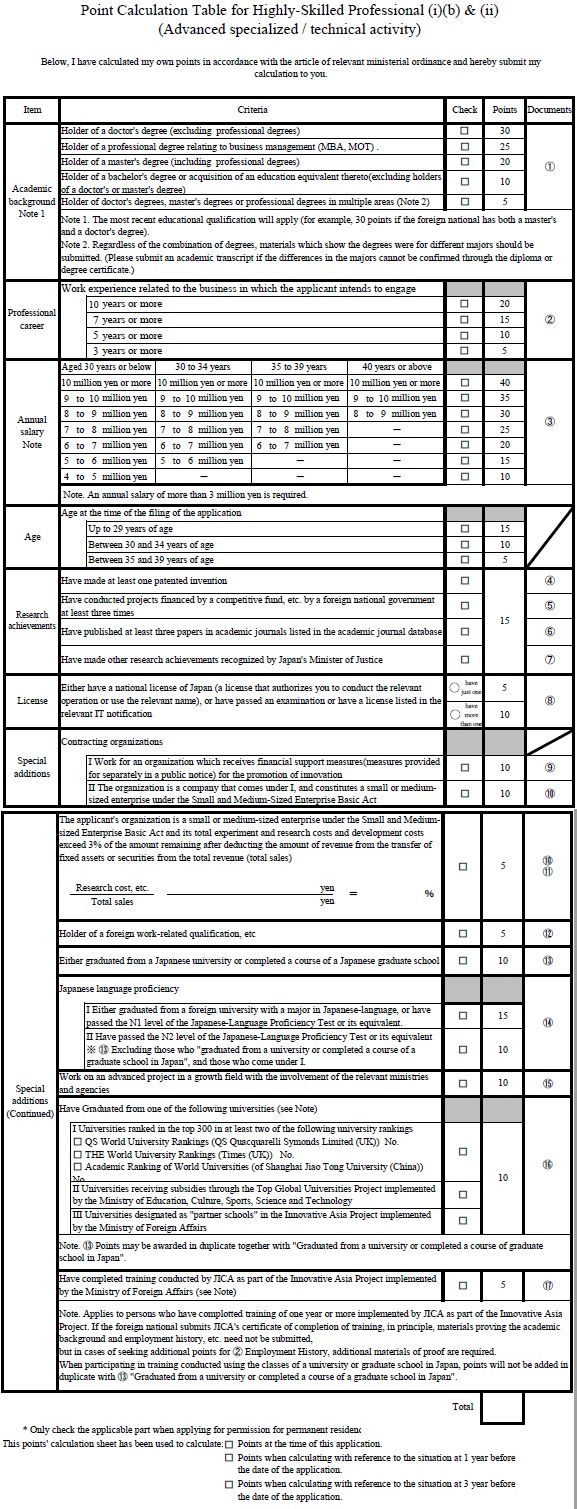
3.Employment-Based (EB)
People with job skills wanted by Japan’s employers are also eligible for permanent residence: Working visas such as Engineers/Humanities Specialists/International Services, Business Managers, Attorneys at Law/CPA, Medical Doctors, Researchers, Lecturers, Intra-Company Transferees, Entertainers, Skilled Laborers and so on.
Screening Criteria
(1) The person is of good conduct.
The person always observes Japanese laws. The person’s daily living as a resident does not invite any social criticism. (S)he has been never sentenced to a fine or imprisonment.
(2) The person has sufficient assets or ability to make an independent living.
The person does not financially depend on someone in the society in his/her daily life, and his/her assets or ability, etc. are assumed to continue to provide him/her with a stable base of livelihood into the future. A stable livelihood is assessed by a unit of a family household, not by the person alone.
(3) The person’s permanent residence is regarded to be in accord with the interests of Japan.
– Undesirable foreign people will be against Japan’s public interests, such as people against Japanese culture, economy, and socially accepted idea. The person fulfills public duties such as tax payment and health insurance. There is no possibility that the person could do harm from the viewpoint of protection of public health.
Eligibility for Your Staying Period in Japan
The period of the person’s current visa (status of residence) must be the maximum period or at least 3 years of stay to be allowed.
In principle to get a permanent visa (status of residence), the person must keep staying in Japan for more than 10 years consecutively. Consecutive ten-year staying in Japan must include more than five-year working visas.
Checklist of Forms and Necessary Documents.
Different from that of Immediate Relatives (Introduction to Permanent Japan Residence [2]+, the applicant must submit a petition that is like an explanatory statement to need a permanent visa at any cost. It includes a family situation, personal history, and your plan to do after getting the permanent visa.
You will need to assemble the following:
FORM
□ Form 34: Application for Permanent Residence (in Japanese) http://www.moj.go.jp/content/000099654.xls
□ One photograph: 40mm long and 30mm broad, taken within 3 months before, clear front face without a hat, white/blue background, your name on the back side, and attach to Form 34
□ Form Guarantee: with guarantor’s signature or seal http://www.moj.go.jp/content/000007381.pdf
(Note) Guarantor must assure your living expenses during stay in Japan, flight expense to return home, and full compliance with the Japanese laws.
Documents
□ One residence certificate including you and your whole family living together 世帯(せたい)全員(ぜんいん)の住民票(じゅうみんひょう) if you have a family, except for your ID number マイナンバー(まいなんばー).
□ Your job certificate:
If you are an employee, one employment certificate from your company.
If you are a self-employed person, one copy of final tax returns 確定申告書(かくていしんこくしょ)の控(ひか)えfrom tax office and one copy of business license certificate when needed.
□ Your residence tax certificates: taxation certificates 課税(かぜい)証明書(しょうめいしょ) and tax payment certificates 納税(のうぜい)証明書(しょうめいしょ) for the latest 3 consecutive years from a city/ward office.
□ Your bank statement/balance certificate or one photocopy of bankbook (cover and recent transactions) preferably
□ One photocopy of your passport and passport itself
□ One photocopy of your Residence Card and Residence Card itself
□ Guarantor’s job certificate (refer to ” Your job certificate” above
□ Guarantor’s income certificate 所得(しょとく)証明書(しょうめいしょ)for the latest one year from a city/ward office
□ Guarantor’s residence certificate 住民票(じゅうみんひょう)
(Note) All certificates above are within 3 months before.
□ A certificate of your contribution to Japan if you have, such as awards, thanks letter, decorations, recommendation letters.


.jpg)
-1.jpg)